*Cube-Host– full cloud services!!
*Cube-Host– full cloud services!!

Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security is your first real security layer on a Windows Server. A correct firewall policy reduces attacks, prevents accidental exposure, and makes troubleshooting easier when you know exactly what is allowed.
This guide is written for a public-facing server: a Windows VPS on VPS hosting, where “open everything” is never a safe default.
Windows Firewall has three profiles. On most VPS deployments, the active profile is Public. A secure baseline is:
# View current profile settings
Get-NetFirewallProfile | Select Name, Enabled, DefaultInboundAction, DefaultOutboundAction
# Enable firewall for all profiles (recommended)
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain,Private,Public -Enabled True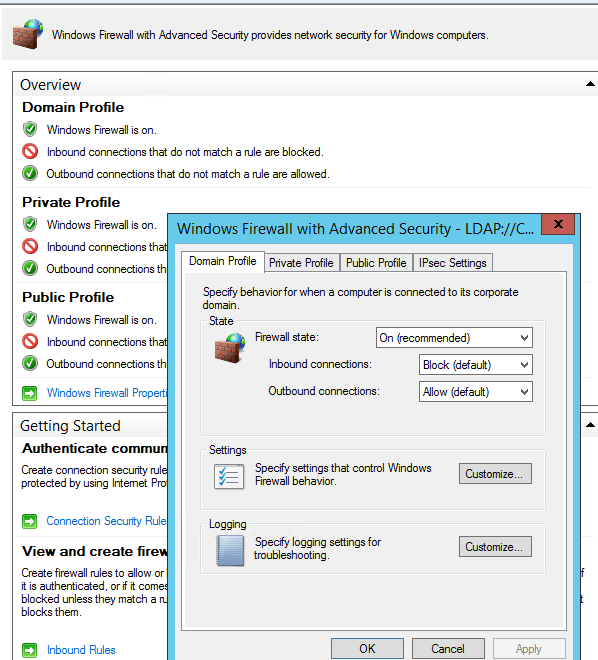
RDP is necessary for administration, but it’s also one of the most scanned ports on the internet. The safe approach:
Important: Always keep a provider console / emergency access option ready before tightening RDP rules to avoid locking yourself out.
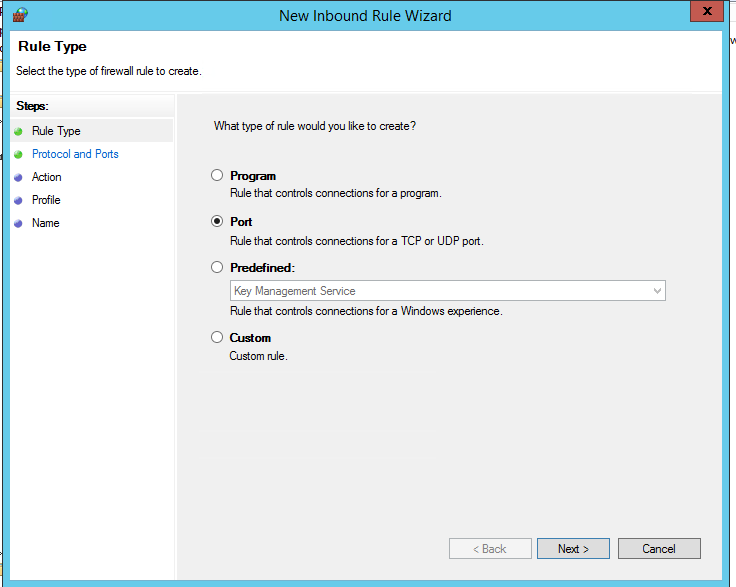
# Replace x.x.x.x with your public IP address
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "RDP (3389) - My IP only" `
-Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 3389 `
-Action Allow -RemoteAddress x.x.x.xCreate explicit rules for services you really use. Typical examples on a Windows VPS:
# Web traffic
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "HTTP (80)" -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 80 -Action Allow
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "HTTPS (443)" -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 443 -Action Allow
# Example: SQL Server on 1433 restricted to a management subnet
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "SQL Server (TCP 1433) - Office" `
-Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 1433 `
-Action Allow -RemoteAddress 203.0.113.0/24When possible, prefer a Program rule for server applications because it ties the permission to a specific executable. Port rules are simpler and common for servers, but they can unintentionally allow unexpected apps listening on the same port.
For custom apps and automation, use Scope (RemoteAddress) to limit who can reach the service.
Logging shows what is being blocked and what is being allowed. This is extremely useful when users say “it doesn’t connect”.
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain,Private,Public `
-LogFileName "C:\Windows\System32\LogFiles\Firewall\pfirewall.log" `
-LogMaxSizeKilobytes 32768 `
-LogAllowed True `
-LogBlocked Truepfirewall.log for blocked connections.# From a client/jump host
Test-NetConnection <server-ip-or-hostname> -Port 443
Test-NetConnection <server-ip-or-hostname> -Port 3389PowerShell (NetSecurity module) is recommended on modern Windows Server. But in some legacy scripts you may still see netsh advfirewall.
# Example: enable built-in Remote Desktop rule group
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="remote desktop" new enable=YesA secure Windows Server firewall strategy is simple and effective: block inbound by default, allow only required services, restrict management ports by IP, and enable logging for visibility.
For production workloads, deploy on a reliable Windows VPS with predictable networking on VPS hosting — and keep your firewall rules minimal, documented, and easy to audit.